14 Conditional Logic
In the Principles of Programming section, we talked about Conditional Logic.

In Python, we apply conditional logic using IF / ELIF / ELSE statements. Let’s see how it works.
Let’s imagine we want to check someone’s age to determine whether they should be sent to room A or room B of our clinic :

Note the tab indentations - these are important as they indicate a block of code. In this case, there are two blocks of code - one to run if the patient age is less than 60, one to run if that’s not the case. In this case, each block is a single line of code, but blocks can be as long as we need.
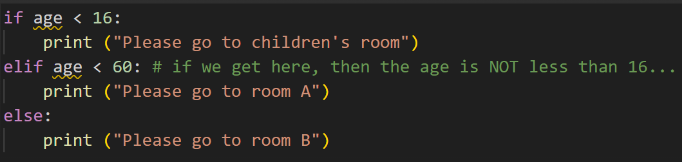
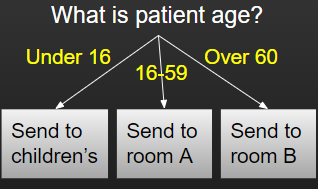
Let’s try running this with some different age variables to see the impact!
If we provide an invalid option - here we provide a name as a string instead - then running the code will give us an error because it doesn’t know how to compare a string (the name) to an integer (the bit on the right of our comparison operator (16)).
14.1 Comparison Operators
There are many comparison operators in Python. We use these to express relational statements that resolve to a Boolean - True or False. They are therefore used in conditional logic.
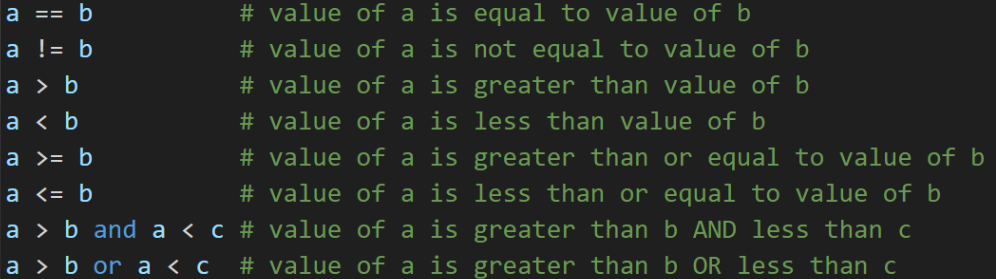
You won’t be able to play along, but have a watch of this game of ‘comparison operators’ to learn more about comparisons.
